KikuchiAikenHDR Material: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with '{{CommandManualMenu}} This command is used to construct a uniaxial KikuchiAikenHDR material object. This material model produces nonlinear hysteretic curves of high damping rubb...') |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
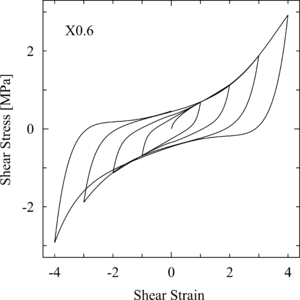
EXAMPLE: | EXAMPLE: | ||
[[Image:KikuchiAikenHDR_StressStrain.png]] | [[Media:KikuchiAikenHDR_sample.tcl|KikuchiAikenHDR_sample.tcl]] | ||
[[Image:KikuchiAikenHDR_StressStrain.png|300px]] | |||
Revision as of 23:29, 30 May 2013
- Command_Manual
- Tcl Commands
- Modeling_Commands
- model
- uniaxialMaterial
- ndMaterial
- frictionModel
- section
- geometricTransf
- element
- node
- sp commands
- mp commands
- timeSeries
- pattern
- mass
- block commands
- region
- rayleigh
- Analysis Commands
- Output Commands
- Misc Commands
- DataBase Commands
This command is used to construct a uniaxial KikuchiAikenHDR material object. This material model produces nonlinear hysteretic curves of high damping rubber bearings (HDRs).
| uniaxialMaterial KikuchiAikenHDR $matTag $tp $ar $hr <-coGHU $cg $ch $cu> <-coMSS $rs $rf> |
| $matTag | integer tag identifying material |
| $tp | rubber type (see note 1) |
| $ar | area of rubber [unit: m^2] (see note 2) |
| $hr | total thickness of rubber [unit: m] (see note 2) |
| $cg $ch $cu | correction coefficients for equivalent shear modulus ($cg), equivalent viscous daming ratio ($ch), ratio of shear force at zero displacement ($cu). |
| $rs $rf | reduction rate for stiffness ($rs) and force ($rf) (see note 3) |
NOTES:
1) Following rubber types for $tp are available:
| X0.6 | Bridgestone X0.6, standard compressive stress |
| X0.6-0MPa | Bridgestone X0.6, zero compressive stress |
2) This material uses SI unit in calculation formula. $ar and $hr must be converted into [m^2] and [m], respectively.
3) $rs and $rf are available if this material is applied to multipleShearSpring (MSS) element. Recommended values are $rs=1/sum(i=0,n-1){ sin(n*i/pi)^2} and $rf=1/sum(i=0,n-1){sin(n*i/pi)}, where n is the number of springs in the MSS. For example, when n=8, $rs=0.2500, $rf=0.1989.
EXAMPLE: