|
|
| Objectives
|
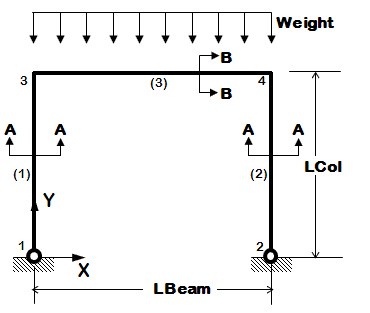
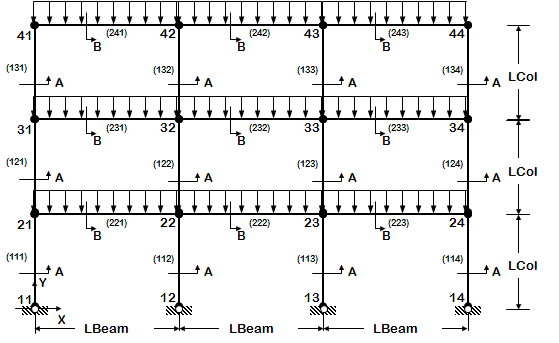
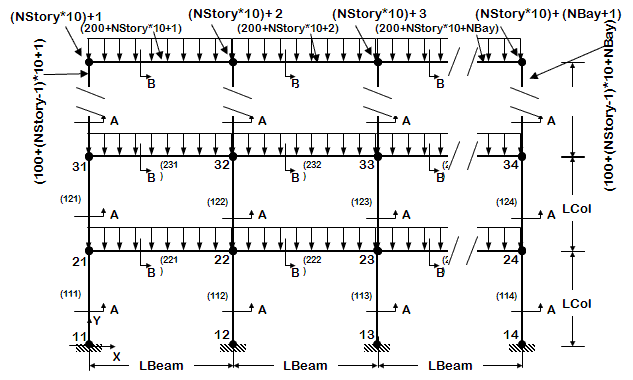
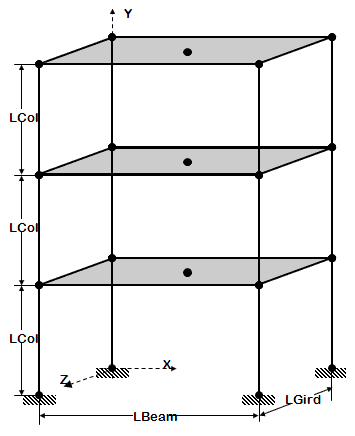
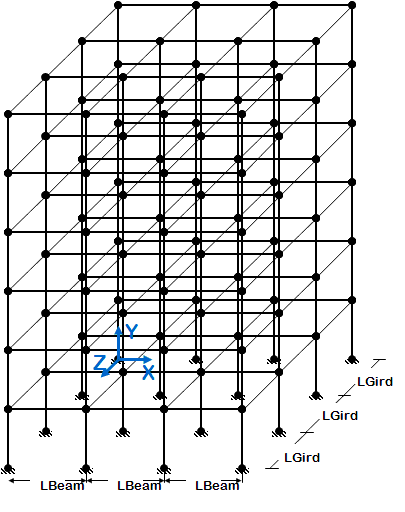
- 3D frame of fixed geometry
- nodes and elements are manually manually, one by one
- introduce rigid floor diaphragm
- use previously-defined procedures to view model node numbers and elements, deformed shape, and displacement history, in 3D
|
|
| Models
|
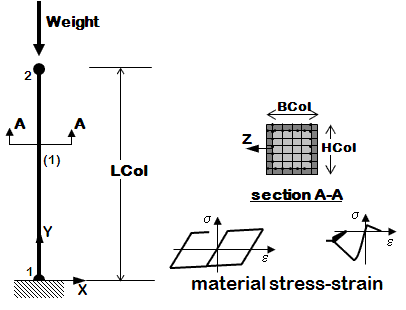
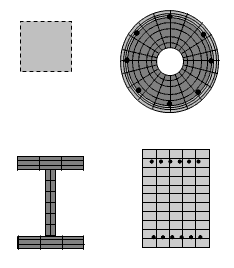
- Reinforced-Concrete Section
- Steel W-Section
- Elastic or Fiber Section option is a variable within one input file
- rigid diaphragm
|
|
| Analyses
|
- static reversed cyclic analysis
- dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation)
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
- dynamic sine-wave input analysis (multiple-support excitation)
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (multiple-support excitation)
- dynamic bidirectional earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
|
|