OpenSees Examples Manual -- Structural Models & Anlyses: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ||
<big><big>Introduction | <big><big>Introduction</big></big></h1> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div> | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
{| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ||
<big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- Introductory Examples]] | <big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- Introductory Examples]]</big></big></h1> | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
{| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ||
<big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- Simple Nonlinear Analysis Examples]] | <big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- Simple Nonlinear Analysis Examples]]</big></big></h1> | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 274: | Line 274: | ||
{| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ||
<big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- 2D Structural Modelling & Analysis Examples]] | <big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- 2D Structural Modelling & Analysis Examples]]</big></big></h1> | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 503: | Line 503: | ||
{| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ||
<big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- 3D Structural Modelling & Analysis Examples]] | <big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- 3D Structural Modelling & Analysis Examples]]</big></big></h1> | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 626: | Line 626: | ||
{| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; border:1px solid #black; background:#white;" | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ! style="padding:2px" | <h1 style="margin:3px; background:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #black; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> | ||
<big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- Section Modelling And Analysis Examples]] | <big><big>[[OpenSees Examples -- Section Modelling And Analysis Examples]]</big></big></h1> | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 03:56, 10 November 2009
Introduction |
|---|
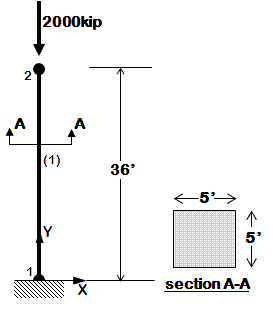
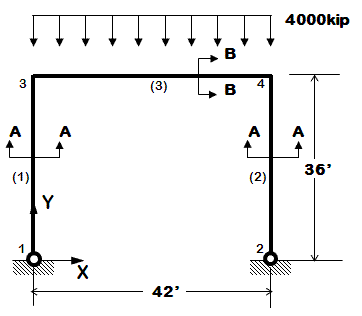
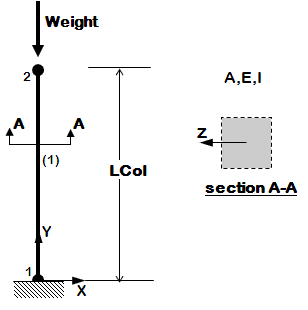
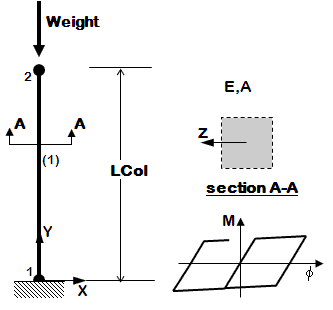
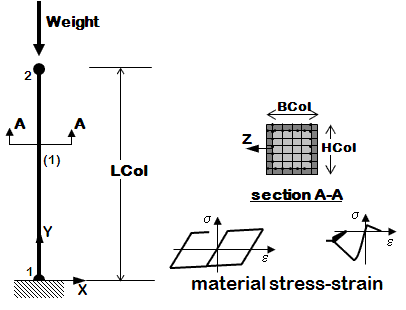
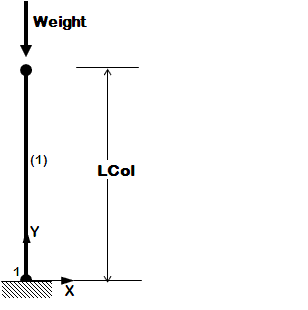
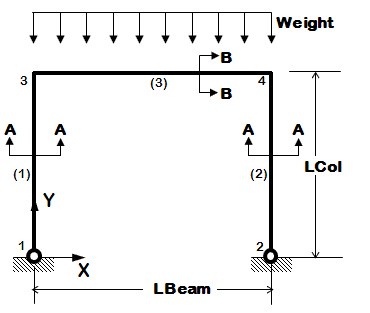
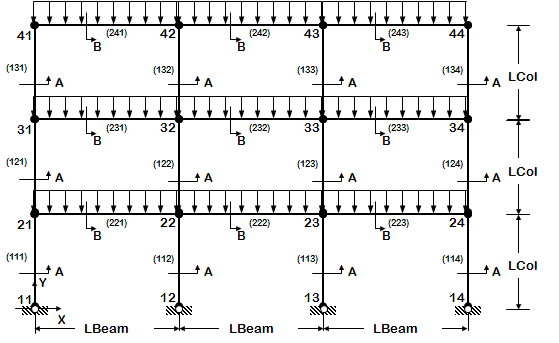
The following examples are listed in order of simplicity. NOTE: gravity analysis is always included as part of the model building |
OpenSees Examples -- Introductory Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSees Examples -- Simple Nonlinear Analysis Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSees Examples -- 2D Structural Modelling & Analysis Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSees Examples -- 3D Structural Modelling & Analysis Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSees Examples -- Section Modelling And Analysis Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Return to OpenSees User