OpenSees Examples Manual -- Structural Models & Anlyses: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<big><big>Introduction</big></big></h1> | <big><big>Introduction</big></big></h1> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
The following examples are listed in order of simplicity. | The following examples are listed in order of simplicity. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
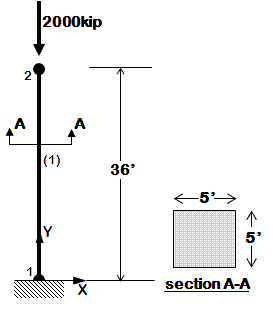
<big>[[OpenSees Example 1a. 2D Elastic Cantilever Column ]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 1a. 2D Elastic Cantilever Column ]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
<!-- 4 COLUMNS --> | <!-- 4 COLUMNS --> | ||
{| style="margin:0; background:none;" | {| style="margin:0; background:none;border:1px solid #black; " | ||
<!-- Column 1 image --> | <!-- Column 1 image --> | ||
| style="margin:0; style="width:25%; border:1px solid #black; background:#white; vertical-align:top;" | | | style="margin:0; style="width:25%; border:1px solid #black; background:#white; vertical-align:top;" | | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*overview of basic OpenSees input structure | *overview of basic OpenSees input structure | ||
*coordinates, boundary conditions, element connectivity, nodal masses, nodal loads, etc. | *coordinates, boundary conditions, element connectivity, nodal masses, nodal loads, etc. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*elastic elements | *elastic elements | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static pushover | *static pushover | ||
*dynamic earthquake-input | *dynamic earthquake-input | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 2 --> | <!-- subSECTION 2 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
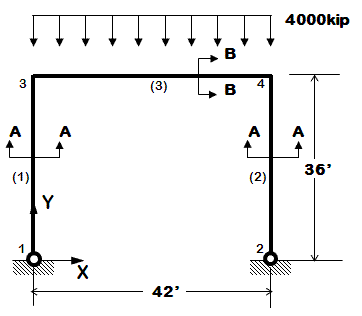
<big>[[OpenSees Example 1b. Elastic Portal Frame]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 1b. Elastic Portal Frame]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example1b_Figure1.gif|link=OpenSees Example 1b. Elastic Portal Frame]]</div> | [[File:Example1b_Figure1.gif|link=OpenSees Example 1b. Elastic Portal Frame]]</div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*two element types | *two element types | ||
*distributed element loads | *distributed element loads | ||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*elastic elements | *elastic elements | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static pushover | *static pushover | ||
*dynamic earthquake-input | *dynamic earthquake-input | ||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
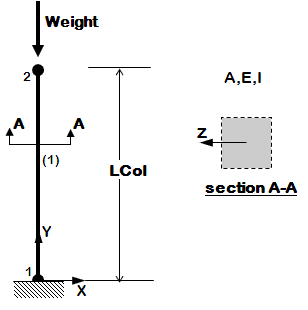
<big>[[OpenSees Example 2a. Elastic Cantilever Column with variables]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 2a. Elastic Cantilever Column with variables]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example2a_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 2a. Elastic Cantilever Column with variables]] | [[File:Example2a_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 2a. Elastic Cantilever Column with variables]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*introduce variable: define & use | *introduce variable: define & use | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*elastic element | *elastic element | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static pushover | *static pushover | ||
*dynamic earthquake-input | *dynamic earthquake-input | ||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 2 --> | <!-- subSECTION 2 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
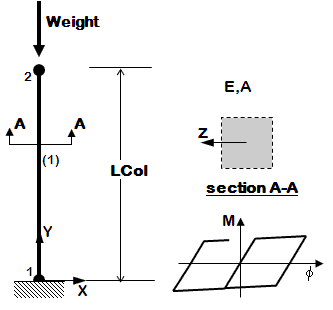
<big>[[OpenSees Example 2b. Nonlinear Cantilever Column: Uniaxial Inelastic Section]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 2b. Nonlinear Cantilever Column: Uniaxial Inelastic Section]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 184: | Line 184: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example2b_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 2b. Nonlinear Cantilever Column: Uniaxial Inelastic Section]] | [[File:Example2b_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 2b. Nonlinear Cantilever Column: Uniaxial Inelastic Section]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 193: | Line 193: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
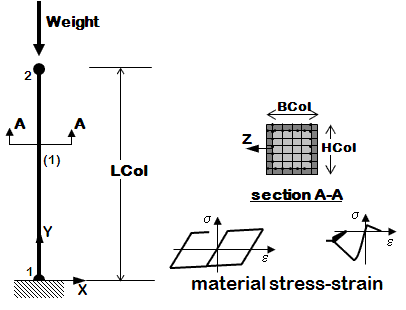
*first example of nonlinear model, set nonlinearity at section level | *first example of nonlinear model, set nonlinearity at section level | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 202: | Line 202: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*nonlinearBeamColumn element | *nonlinearBeamColumn element | ||
*uniaxial section | *uniaxial section | ||
| Line 212: | Line 212: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static pushover | *static pushover | ||
*dynamic earthquake-input | *dynamic earthquake-input | ||
| Line 223: | Line 223: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 3 --> | <!-- subSECTION 3 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
<big>[[OpenSees Example 2c. Nonlinear Cantilever Column: Inelastic Uniaxial Materials in Fiber Section ]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 2c. Nonlinear Cantilever Column: Inelastic Uniaxial Materials in Fiber Section ]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 234: | Line 234: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example2c_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 2c. Nonlinear Cantilever Column: Inelastic Uniaxial Materials in Fiber Section ]] | [[File:Example2c_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 2c. Nonlinear Cantilever Column: Inelastic Uniaxial Materials in Fiber Section ]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 243: | Line 243: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*set nonlinearity at material level | *set nonlinearity at material level | ||
*material stress-strain response is assembled into fiber section | *material stress-strain response is assembled into fiber section | ||
| Line 254: | Line 254: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*nonlinearBeamColumn element | *nonlinearBeamColumn element | ||
*uniaxial material | *uniaxial material | ||
| Line 265: | Line 265: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static pushover | *static pushover | ||
*dynamic earthquake-input | *dynamic earthquake-input | ||
| Line 277: | Line 277: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
<big>[[OpenSees Example 3. Cantilever Column with units]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 3. Cantilever Column with units]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 288: | Line 288: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example3_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 3. Cantilever Column with unit]] | [[File:Example3_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 3. Cantilever Column with unit]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 297: | Line 297: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
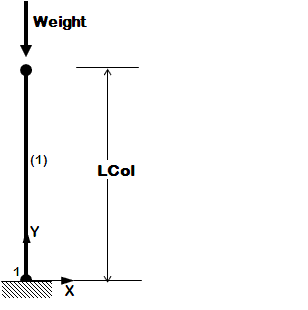
*units, defined and used (they will be used in all subsequent examples) | *units, defined and used (they will be used in all subsequent examples) | ||
*separate model-building and analysis files | *separate model-building and analysis files | ||
| Line 308: | Line 308: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*elastic elements | *elastic elements | ||
*inelastic uniaxial section | *inelastic uniaxial section | ||
| Line 320: | Line 320: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static pushover | *static pushover | ||
*dynamic earthquake-input | *dynamic earthquake-input | ||
| Line 331: | Line 331: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 2 --> | <!-- subSECTION 2 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
<big>[[OpenSees Example 4. Portal Frame]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 4. Portal Frame]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 342: | Line 342: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example4_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 4. Portal Frame]] | [[File:Example4_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 4. Portal Frame]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 351: | Line 351: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
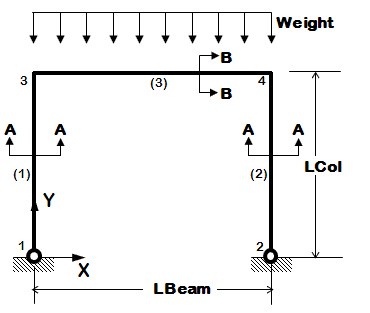
*use previously-defined procedures to simplify input | *use previously-defined procedures to simplify input | ||
*introduce more analysis types | *introduce more analysis types | ||
| Line 362: | Line 362: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*elastic elements | *elastic elements | ||
*inelastic uniaxial section | *inelastic uniaxial section | ||
| Line 373: | Line 373: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static reversed cyclic analysis | *static reversed cyclic analysis | ||
*dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | *dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | ||
| Line 388: | Line 388: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 3 --> | <!-- subSECTION 3 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
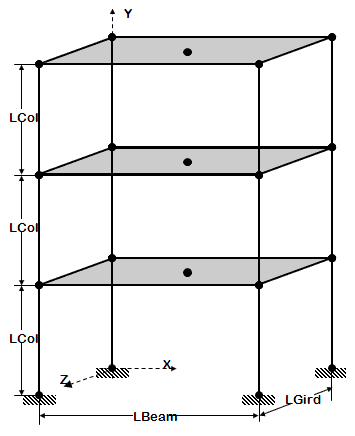
<big>[[OpenSees Example 5. 2D Frame, 3-story 3-bay, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 5. 2D Frame, 3-story 3-bay, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 399: | Line 399: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example5_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 5. 2D Frame, 3-story 3-bay, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]] | [[File:Example5_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 5. 2D Frame, 3-story 3-bay, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 408: | Line 408: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*2D frame of fixed geometry: 3-story, 3-bay | *2D frame of fixed geometry: 3-story, 3-bay | ||
*nodes and elements are defined manually, one by one | *nodes and elements are defined manually, one by one | ||
| Line 418: | Line 418: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*Reinforced-Concrete Section | *Reinforced-Concrete Section | ||
*Steel W-Section | *Steel W-Section | ||
| Line 431: | Line 431: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static reversed cyclic analysis | *static reversed cyclic analysis | ||
*dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | *dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | ||
| Line 446: | Line 446: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 4 --> | <!-- subSECTION 4 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
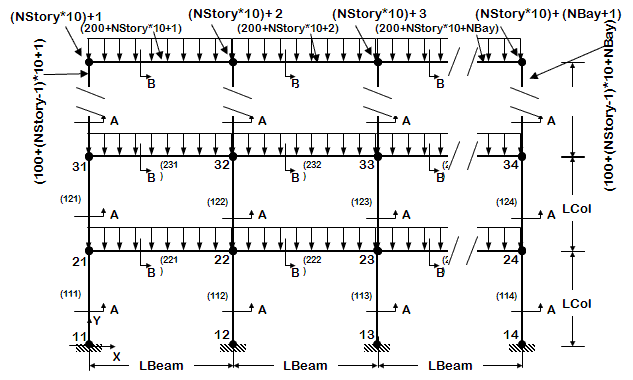
<big>[[OpenSees Example 6. generic 2D Frame, N-story N-bay, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 6. generic 2D Frame, N-story N-bay, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 457: | Line 457: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example6_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 6. generic 2D Frame, N-story N-bay, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]] | [[File:Example6_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 6. generic 2D Frame, N-story N-bay, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 466: | Line 466: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
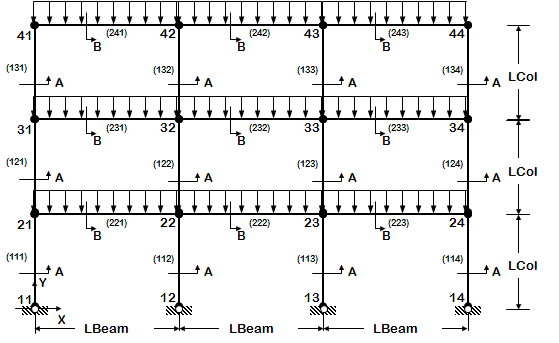
*2D frame geometry of variable geometry ( # stories and # bays are variables) | *2D frame geometry of variable geometry ( # stories and # bays are variables) | ||
*node and element definition is automated | *node and element definition is automated | ||
| Line 477: | Line 477: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*Reinforced-Concrete Section | *Reinforced-Concrete Section | ||
*Steel W-Section | *Steel W-Section | ||
| Line 490: | Line 490: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static reversed cyclic analysis | *static reversed cyclic analysis | ||
*dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | *dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | ||
| Line 506: | Line 506: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
<big>[[OpenSees Example 7. 3D Frame, 3-story 3-bayX 3-bayZ, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 7. 3D Frame, 3-story 3-bayX 3-bayZ, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 517: | Line 517: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example7_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 7. 3D Frame, 3-story 3-bayX 3-bayZ, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]] | [[File:Example7_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 7. 3D Frame, 3-story 3-bayX 3-bayZ, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 526: | Line 526: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*3D frame of fixed geometry | *3D frame of fixed geometry | ||
*nodes and elements are manually manually, one by one | *nodes and elements are manually manually, one by one | ||
| Line 538: | Line 538: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*Reinforced-Concrete Section | *Reinforced-Concrete Section | ||
*Steel W-Section | *Steel W-Section | ||
| Line 550: | Line 550: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static reversed cyclic analysis | *static reversed cyclic analysis | ||
*dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | *dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | ||
| Line 565: | Line 565: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 2 --> | <!-- subSECTION 2 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
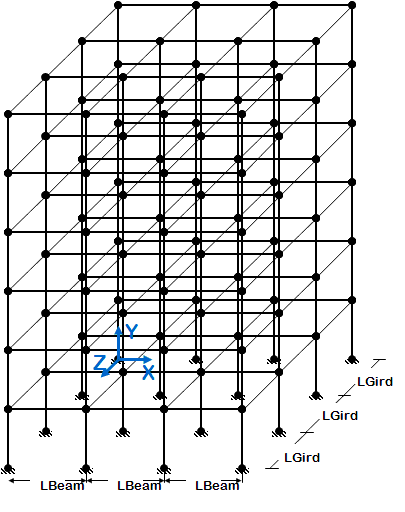
<big>[[OpenSees Example 8. generic 3D Frame, NStory NBayX NBayZ, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 8. generic 3D Frame, NStory NBayX NBayZ, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 576: | Line 576: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example8_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 8. generic 3D Frame, NStory NBayX NBayZ, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]] | [[File:Example8_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 8. generic 3D Frame, NStory NBayX NBayZ, Reinforced-Concrete Section & Steel W-Section]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 585: | Line 585: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*3D frame geometry of variable geometry ( # stories and # bays in X and Z are variables) | *3D frame geometry of variable geometry ( # stories and # bays in X and Z are variables) | ||
*node and element definition is automated | *node and element definition is automated | ||
| Line 596: | Line 596: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*Reinforced-Concrete Section | *Reinforced-Concrete Section | ||
*Steel W-Section | *Steel W-Section | ||
| Line 608: | Line 608: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*static reversed cyclic analysis | *static reversed cyclic analysis | ||
*dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | *dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) | ||
| Line 629: | Line 629: | ||
<!-- subSECTION 1 --> | <!-- subSECTION 1 --> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
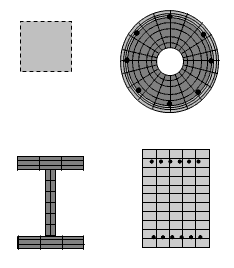
<big>[[OpenSees Example 9. Build & Analyze a Section Example]]</big> | <big>[[OpenSees Example 9. Build & Analyze a Section Example]]</big> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 640: | Line 640: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | | ! style="padding:2px" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
[[File:Example9_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 9. Build & Analyze a Section Example]] | [[File:Example9_figure1.GIF|link=OpenSees Example 9. Build & Analyze a Section Example]] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 649: | Line 649: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Objectives</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*defined section using uniaxial behavior (define moment-curvature curve) or | *defined section using uniaxial behavior (define moment-curvature curve) or | ||
*define section using uniaxial materials (define stress curve) in fiber section | *define section using uniaxial materials (define stress curve) in fiber section | ||
| Line 659: | Line 659: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Models</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*Uniaxial Nonlinear section | *Uniaxial Nonlinear section | ||
*Fiber Steel W-section | *Fiber Steel W-section | ||
| Line 673: | Line 673: | ||
! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ! style="padding:2px" | <strong>Analyses</strong> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="color:#000;" | <div > | | style="color:#000;" | <div> | ||
*2D static unidirectional moment-curvature analysis | *2D static unidirectional moment-curvature analysis | ||
*3D static unidirectional moment-curvature analysis | *3D static unidirectional moment-curvature analysis | ||
Revision as of 03:52, 10 November 2009
Introduction |
|---|
The following examples are listed in order of simplicity. NOTE: gravity analysis is always included as part of the model building |
OpenSees Examples -- Introductory Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSees Examples -- Simple Nonlinear Analysis Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSees Examples -- 2D Structural Modelling & Analysis Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSees Examples -- 3D Structural Modelling & Analysis Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSees Examples -- Section Modelling And Analysis Examples |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Return to OpenSees User