HDR
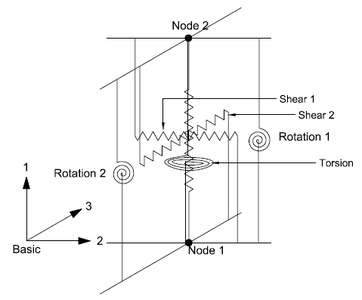
This command is used to construct an HDR bearing element object in three-dimension. The 3D continuum geometry of an high damping rubber bearing is modeled as a 2-node, 12 DOF discrete element. This is the third element in the series of elements developed for analysis of base-isolated structures under extreme loading (others being [ElastomericX] and [LeadRubberX]). The major difference between HDR element with [ElastomericX] and [LeadRubberX] is the hysteresis model in shear. The HDR element uses the model proposed by Grant et al. (2004) to capture the shear behavior of a high damping rubber bearing.
The syntax of command to use this element in a 3D problem:
| element ElastomericX $eleTag $Nd1 $Nd2 $qRubber $uh $Gr $Kbulk $D1 $D2 $ts $tr $n $a1 $a2 $a3 $b1 $b2 $b3 $c1 $c2 $c3 $c4 <<$x1 $x2 $x3> $y1 $y2 $y3> <$kc> <$PhiM> <$ac> <$sDratio> <$m> <$cd> <$tc> |
| $eleTag | unique element object tag |
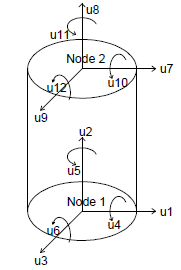
| $Nd1 $Nd2 | end nodes |
| $qRubber | yield strength |
| $uh | yield deformation |
| $Gr | shear modulus of elastomeric bearing |
| $Kbulk | bulk modulus of rubber |
| $D1 | internal diameter |
| $D2 | outer diameter (excluding cover thickness) |
| $ts | single steel shim layer thickness |
| $tr | single rubber layer thickness |
| $n | number of rubber layers |
| $a1 $a2 $a3 $b1 $b2 $b3 $c1 $c2 $c3 $c4 | parameters of Grant model |
| $x1 $x2 $x3 | vector components in global coordinates defining local x-axis (optional) |
| $y1 $y2 $y3 | vector components in global coordinates defining local y-axis (optional) |
| $kc | cavitation parameter (optional, default = 10.0) |
| $PhiM | damage parameter (optional, default = 0.5) |
| $ac | strength reduction parameter (optional, default = 1.0) |
| $sDratio | shear distance from iNode as a fraction of the element length (optional, default = 0.5) |
| $m | element mass (optional, default = 0.0) |
| $cd | viscous damping parameter (optional, default = 0.0) |
| $tc | cover thickness (optional, default = 0.0) |
An example use of this element can be found here: to be updated!
References
- Kumar, M., Whittaker, A., and Constantinou, M. (2014). "An advanced numerical model of elastomeric seismic isolation bearings." Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, Published online, DOI: 10.1002/eqe.2431. Link
- Grant, D. N., Fenves, G. L., and Whittaker, A. S. (2004). "Bidirectional modeling of high-damping rubber bearings." Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 8(sup001), 161-185.